AggLayer and Pessimistic Proofs
With the recent update to AggLayer v0.2, a pessimistic transaction verification mechanism (Pessimistic Proofs) has been introduced, offering a different approach to solving trust issues between blockchains.

Most cross-chain solutions rely on Optimistic Proofs, assuming that participants act honestly — until proven otherwise. This is the foundation of Optimistic Rollups.
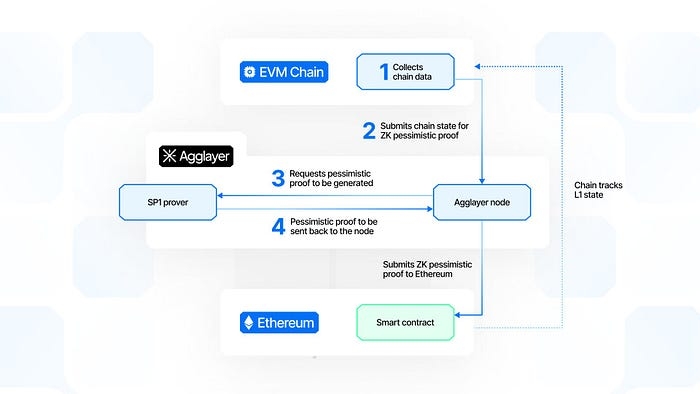
Instead, AggLayer adopts a pessimistic model, where every blockchain is considered potentially unreliable by default. Before confirming a cross-chain operation, the system verifies all input data. If a valid proof cannot be formed, the transaction fails.
The primary goals of Pessimistic Proofs are to ensure:
➡️ Every cross-chain transaction is backed by a real deposit.
➡️ No chain can withdraw more than it has deposited.
➡️ Even if one chain is compromised, others remain unaffected.
The model is built around a Unified Bridge and state trees that track each transaction:
1️⃣ Local Exit Tree — Each blockchain generates an exit tree recording all outgoing transactions.
2️⃣ Global Exit Root — A globally aggregated state stored on Ethereum, consolidating all local exit trees.
3️⃣ Nullifier Tree — A control system preventing duplicate withdrawal requests.
Before executing a cross-chain transfer, the pessimistic proof verifies:
✅ Does the network state match the declared one?
✅ Are there sufficient funds for the withdrawal?
✅ Is the balance integrity maintained within the global bridge?
If any condition fails, the atomic transaction does not proceed — effectively stopping bridge attacks before they can be executed.
In practice, this update has led to several key improvements:
🔹 Expanded support for any blockchain.
Previously, only Polygon CDK-based blockchains could interact with AggLayer. Now, even chains without ZK-proofs can connect, with security ensured via Pessimistic Proofs.
🔹 Unified liquidity without wrapped tokens.
Unlike most bridges that rely on wrapped versions of assets, AggLayer v0.2 enables native token transfers across chains without wrapping, reducing risk and simplifying cross-chain operations.
🔹 Flexible choice for blockchains.
Blockchains using Polygon CDK can continue operating under the legacy settlement mechanism, while new networks gain an extra security layer with Pessimistic Proofs.
An important point: if a blockchain initially adopts Pessimistic Proofs, it can later transition to ZK verification if it meets the criteria. However, the reverse transition is not possible.
Final Thoughts
Overall, we view this update positively. There is an ongoing race to develop the most effective cross-chain solution capable of onboarding the maximum number of blockchains. Previously, the requirement to use only ZK rollups significantly limited AggLayer. This pivot might also be motivated by the goal of integrating native Ethereum. We believe AggLayer is well-positioned to compete in this space. Haust Network will be leveraging Pessimistic Proofs within the AggLayer framework to enhance the security and reliability of its cross-chain operations
written by Haust Network CTO Andrew Nalichaev
Last updated